COMMON AGE-RELATED EYE PROBLEMS
When we get older our bodies age and some age-
related eye problems will appear.But we don’t have
to live with age-related vision loss.
COMMON AGE -RELATED EYE PROBLEMS
1.Presbyopia
After the age of 40 ,many people will experience
difficulty in focusing on near objects .
This is due to hardening of the lens inside the eyes.
At the beginning, you can compensate the loss of
focusing ability by holding the reading material
farther away from the eyes.
Later you will need correctives glasses.
Some corrective eye surgery options are available ,
such as Monovision Lasik, Conductive keratoplasty.
2.Dry eye syndrome
Causes:
- heavy digital devices use
- dry environment
- prolonged contact lens wear
- post Lasik surgery
- side effects of medications such as diuretics ,allergy drugs, beta-blockers ,antihistamines
- a diet poor in omega 3 fatty acids
- health conditions – diabetes,lupus ,arthritis
- deficiency of the tear producing glands
Symptoms:
- blurry vision

A blurry photo of a bridge in a forest
- sensitive to light
- irritation to windy condition
- having problem in wearing contact lenses
- scratchy and gritty feeling
- red eyes
Treatment
- check your medications with your doctor
- increase omega 3 fatty acids intake by eating oily
fishes such as salmon and sardines
- stay hydrated
- don’t wear contact lens for prolonged periods and keep them clean
- blink your eyes more often
- When using the computer take breaks.Look away from the screen every 20 minutes at something which is at least 20 feet away
- the use of artificial tears , lubricating eye drops ,
prescribed steroid eye drops
- Wear sunglasses that block 100% of UV rays.
3.Cataract
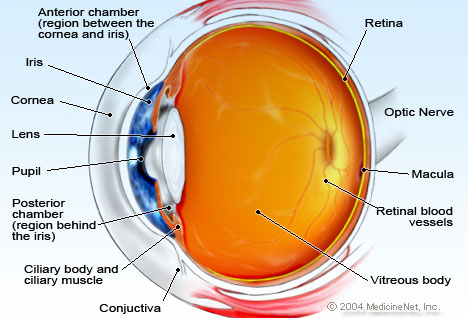
An illustration of the anatomy of an eye
If the lens is not clear the result will be a cloudy image.
In severe cases will lead to blindness.
The lens will become cloudy due to the following reasons.
- aging
- medical conditions– diabetes,high blood pressure,obesity
- trauma or past eye surgery
- Long-term use of steroid medications
- excessive alcohol drinking
- excessive exposure to sunlight
- exposure to ionizing radiation such as X-rays and cancer radiation therapy
- familial history of cataract
- smoking
- previous history of cataract
- smoking
Signs and symptoms:
- blurred or dim vision
- increasing difficulty with vision at night
- sensitive to light and glare
- seeing “halos” around lights
- fading or yellowing of colors in the vision field
Lifestyle change before surgery:
- use accurate prescription eyeglasses or contact lens
- Ensure enough lighting at home
- When going outside during the day wear
sunglasses or a wide -brimmed hat to
reduce glare
- limit night driving
Treatment
– Eye surgery to remove the clouded lens and
replaced with an artificial lens (intraocular lens)
4.Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a condition in which the increased
intraocular pressure causes damage to the optic nerve.
The vision loss will deteriorate until tunnel vision develops .
In the end ,will result in blindness.
The 2 common types of glaucoma
Primary open-angle glaucoma gradually reduces
your peripheral vision without other symptoms.
By the time you notice it, the permanent damage
already has occurred.
Acute angle-closure glaucoma. produces sudden
symptoms such as eye pain, headaches, halos
around lights,dilated pupils,nausea and vomiting and
vision loss

Causes:
- inefficient drainage of aqueous humor causes
the increase of intraocular pressure
- The increased intraocular pressure cause
damage to the optic nerve
Treatment
- measurement of the intraocular pressure
- visual field testing

- glaucoma tunnel vision
- eye drops or medications to reduce the
intraocular pressure
- laser eye surgery if the condition is not controlled
5.Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic Retinopathy is a condition of abnormal
growth of new blood vessels within the retina.
These small blood vessels may leak or break.
The new blood vessels may bleed into the vitreous humor
This bleeding and new growth can cause scarring
or a retinal detachment which will lead to vision loss.
Signs and symptoms
- may be symptomless

- Blurred vision
- floaters
- loss of vision
- blindness
Diagnosis
- dilated-pupil fundus examination
Prevention Tips
- keep blood sugar level within normal limits
- maintain good control of blood pressure
- eat a healthy diet
- regular exercise
- don’t smoke
- have a regular eye examination
Treatment
- Steroid eye drops or intraocular steroid injection
- Laser treatment to seal leaking blood vessels
and eliminate abnormal blood vessels - vitrectomy to remove hemorrhage in the vitreous humor
- anti-vascular endothelial growth factor
medication injection
- The medication reduces the swelling, leakage,and growth of unwanted blood vessel in the retina
6.Macular degeneration
Macular degeneration is deterioration of the macula.
The health of the macula determines our ability to
see fine details.

macular degeneration vision
Prevention
- eat a healthy diet
- regular exercise
- use of sunglasses to protect your eyes from harmful UV rays
- nutritional supplements containing antioxidant ,multivitamins that also contain lutein and zeaxanthin
- maintain a normal body weight
- maintain a normal blood pressure
- avoid smoking
Diagnosis
- viewing a chart of black lines arranged in a graph pattern(Amsler grid)
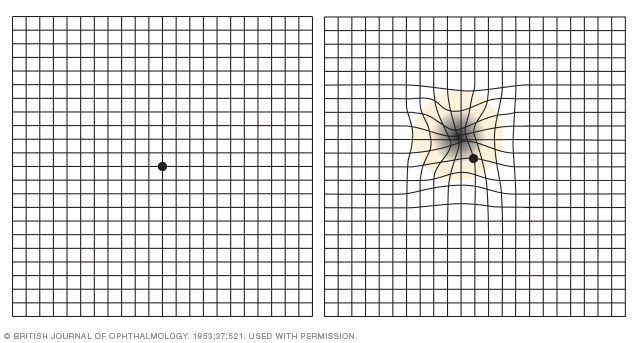
- retinal examination
- Fluorescein angiography
Treatment
- Photodynamic laser therapy.The doctor injects the medication into the bloodstream and
absorbed by the abnormal blood vessels in the eye.
- Then a cold laser is introduced into the eye to activate the drug , damaging the abnormal blood vessels.
- eating a diet high in omega 3
- taking supplements containing lutein and zeaxanthin
7.Floaters
-Floaters are blurry spots or specks in your vision that move.
-They are debris in the eye’s vitreous gel.
-They don’t block vision and are easier to see in bright light.
-Floaters are common and usually harmless.
-But if they appear or increase suddenly, or you also
have light flashes consult a doctor.
-Persistent white or black spots and a sudden
shadow or loss of peripheral vision need immediate
medical attention.
-These could mean a posterior vitreous detachment
or a retinal detachment
Treatment

Comments